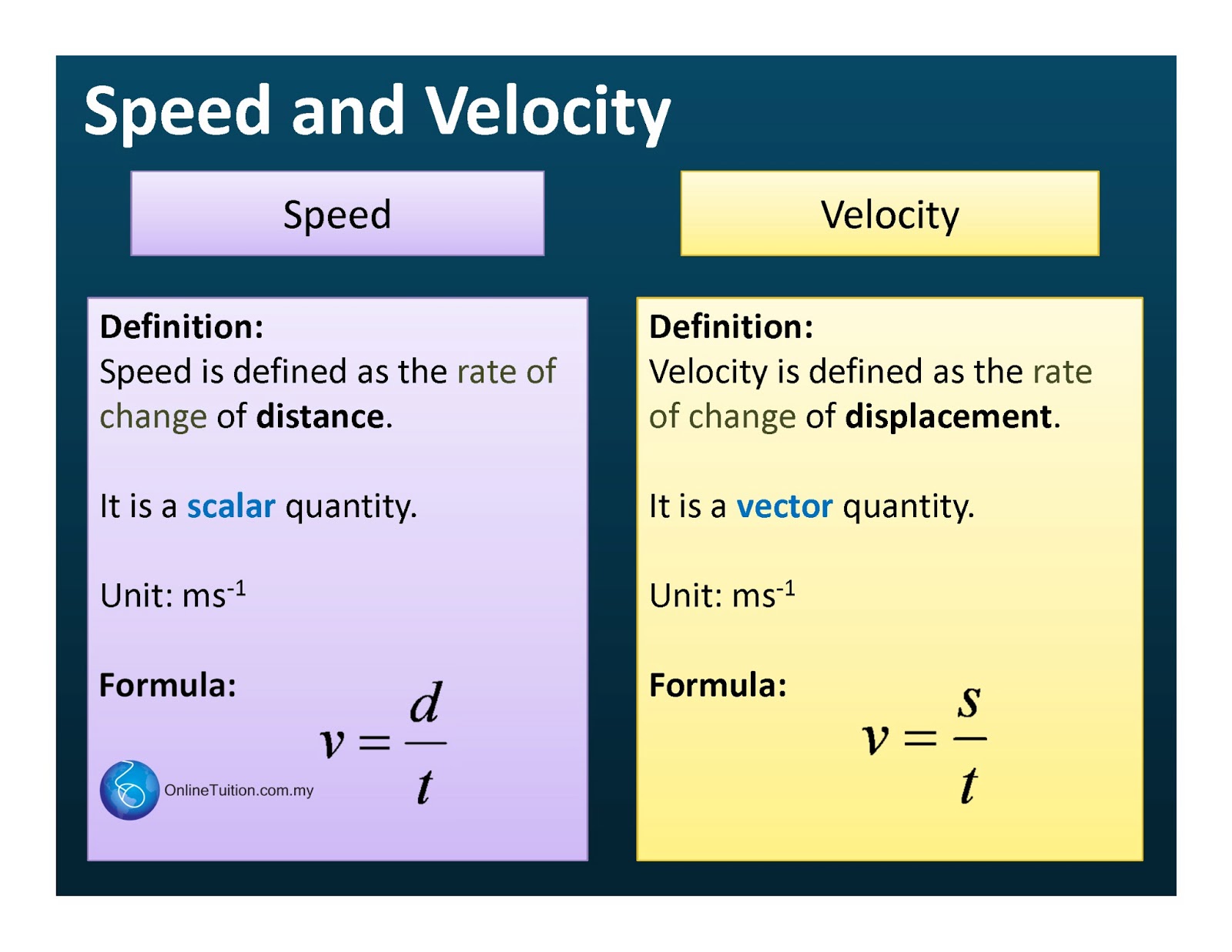
Speed is a concept that fascinates many, from the fast pace of technology to the swiftness of a cheetah on the hunt. It is a fundamental aspect of our world, influencing everything from transportation and sports to biology and physics. Understanding speed examples helps us grasp how quickly things can move, how efficiently tasks can be completed, and how we can harness speed for various applications.
In this article, we delve into various speed examples that illustrate the incredible velocity at which things can occur. By examining these examples, we gain insights into the mechanisms that allow for such rapidity and the implications of speed in different contexts. Whether it's the breakneck speed of a roller coaster or the mind-boggling pace of a supercomputer, speed is a phenomenon that never ceases to amaze.
Our exploration will cover a wide range of topics, providing a comprehensive understanding of speed examples across different domains. From natural phenomena and technological advancements to everyday occurrences, speed is a key element that shapes our experiences and perceptions. Join us as we uncover the secrets behind some of the fastest phenomena in our world.
Table of Contents
- What are the Fastest Animals?
- How Does Speed Manifest in Technology?
- How Fast Can Humans Really Go?
- Speed in Sports: What are the Limits?
- Exploring the Speed of Light
- Transportation: Speed Examples on Land, Sea, and Air
- Biological Speed: How Fast Does Life Operate?
- Physics and Speed: Theories and Realities
- Communication: How Fast is Fast?
- The Speed of Computing: Past, Present, Future
- Entertainment: Where Does Speed Take the Lead?
- Speed and Safety: Where Do They Intersect?
- Historical Speed Milestones
- What Does the Future Hold for Speed?
- FAQs about Speed Examples
- Conclusion
What are the Fastest Animals?
Animals have evolved to reach remarkable speeds, with many species relying on their swiftness for survival. The cheetah, for instance, is renowned for being the fastest land animal, capable of reaching speeds up to 70 mph. This incredible speed is achieved through a combination of lightweight body, flexible spine, and powerful leg muscles. Meanwhile, the peregrine falcon dives at speeds exceeding 200 mph, making it the fastest bird and one of the fastest creatures on Earth.
Other speed examples in the animal kingdom include the sailfish, the fastest marine creature, which can swim at speeds of 68 mph. These rapid movements are crucial for hunting and evading predators. Speed is not just about raw velocity; it's also about precision and timing, as demonstrated by the dragonfly's ability to catch prey mid-air with remarkable agility.
Why is Speed Important for Animals?
- Escaping predators
- Capturing prey
- Migrating efficiently
- Competing for mates
The significance of speed in the animal kingdom cannot be overstated. It often determines an animal's survival and reproductive success. Species that can move quickly are more likely to escape threats and secure food, while those with slower speeds must rely on other strategies, such as camouflage or defensive mechanisms.
How Does Speed Manifest in Technology?
In the realm of technology, speed is synonymous with efficiency and performance. The rapid advancement of technology has led to the development of faster processors, quicker internet connections, and speedier data transfer methods. These improvements have revolutionized industries, from finance to healthcare, enabling tasks that once took hours to be completed in seconds.
One of the most notable speed examples in technology is the evolution of internet speeds. From dial-up connections with speeds of 56 kbps to fiber-optic networks offering gigabit speeds, the internet has become faster and more accessible, transforming the way we communicate, access information, and conduct business.
Technological Advancements Driving Speed
- 5G networks
- Quantum computing
- Solid-state drives
- Machine learning algorithms
These advancements have not only increased speed but also enhanced reliability and security, making technology an integral part of our daily lives. Speed in technology also poses challenges, such as cybersecurity threats, that require innovative solutions to ensure data protection and privacy.
How Fast Can Humans Really Go?
Human speed is a topic of great interest, particularly in the fields of athletics and transportation. The fastest recorded human running speed is 27.8 mph, achieved by Usain Bolt during a 100-meter sprint. This remarkable feat highlights the physical capabilities of humans and the potential for breaking speed barriers through training and innovation.
Beyond athletics, humans have developed vehicles capable of reaching incredible speeds. The Thrust SSC holds the record for the fastest land vehicle, traveling at 763 mph, while the SR-71 Blackbird remains one of the fastest aircraft, reaching speeds of over 2,100 mph.
Factors Influencing Human Speed
- Genetics
- Training and conditioning
- Technological aid
- Environmental conditions
Human speed is not limited to physical movement. It also encompasses cognitive speed, such as reaction times and decision-making processes, which are crucial in various professions and daily activities.
Speed in Sports: What are the Limits?
Speed is a critical factor in many sports, influencing performance and competition outcomes. In track and field, athletes constantly strive to beat world records, showcasing their speed and endurance. The 9.58-second 100-meter dash by Usain Bolt remains a benchmark for sprinters worldwide.
In team sports, such as soccer and basketball, speed contributes to strategic plays and quick reflexes. Players with exceptional speed can change the course of a game, making them valuable assets to their teams.
Speed Training Techniques
- Plyometrics
- Interval training
- Resistance training
- Agility drills
These techniques help athletes improve their speed, agility, and overall performance. However, the pursuit of speed in sports must be balanced with considerations of health and safety, as pushing beyond physical limits can lead to injuries.
Exploring the Speed of Light
The speed of light is one of the most fundamental constants in physics, measured at approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second) in a vacuum. This speed is not just a measure of how fast light travels; it also represents a cosmic speed limit that nothing with mass can exceed.
Understanding the speed of light has profound implications for our comprehension of the universe. It plays a crucial role in Einstein's theory of relativity, which describes how time and space are interconnected. The constancy of the speed of light leads to phenomena such as time dilation and length contraction, which challenge our intuitive understanding of reality.
Applications of Light Speed
- Astronomy and the observation of distant galaxies
- Communication technologies like fiber optics
- GPS satellite synchronization
- Exploration of theoretical concepts, such as wormholes
These applications highlight the importance of the speed of light in both scientific research and practical technologies, demonstrating its far-reaching impact on our lives.
Transportation: Speed Examples on Land, Sea, and Air
Transportation has always been about speed, with each mode of travel striving to reach new velocity milestones. On land, high-speed trains like Japan's Shinkansen and France's TGV offer rapid transit options, reaching speeds of up to 320 km/h (200 mph).
In the air, commercial jets routinely travel at speeds exceeding 900 km/h (560 mph), while military aircraft like the F-22 Raptor can reach speeds over 2,400 km/h (1,500 mph). On the water, hydrofoils and advanced naval vessels achieve impressive speeds, enhancing maritime travel and commerce.
Future of Transportation Speed
- Hyperloop systems
- Electric and autonomous vehicles
- Space tourism and travel
- Green transportation technologies
As technology advances, the future of transportation promises even greater speeds, with innovations that aim to reduce travel times and improve efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
Biological Speed: How Fast Does Life Operate?
Speed in biology is not limited to the physical movement of organisms. It also encompasses the rapid processes occurring at the cellular and molecular levels. For instance, nerve impulses travel at speeds up to 120 meters per second, enabling quick reactions to stimuli.
Enzymatic reactions are another example of biological speed, where catalysts accelerate chemical processes essential for life. These reactions can occur millions of times per second, allowing for the efficient functioning of biological systems.
Biological Processes Influencing Speed
- Metabolic rates
- Genetic factors
- Environmental influences
- Adaptations and evolution
Understanding these processes provides insights into the complexity and efficiency of life, highlighting the intricate balance between speed and regulation within biological systems.
Physics and Speed: Theories and Realities
Speed is a fundamental concept in physics, underlying many theories and phenomena. From classical mechanics to quantum physics, speed is a key variable that influences the behavior of objects and particles. Newton's laws of motion describe how forces affect the speed and direction of objects, providing a basis for understanding motion in everyday life.
In the realm of quantum physics, the speed of subatomic particles challenges our understanding of reality. Particles can exhibit wave-particle duality, existing in multiple states simultaneously, and can be influenced by phenomena such as quantum tunneling, where they pass through barriers at seemingly impossible speeds.
Key Physics Concepts Related to Speed
- Velocity and acceleration
- Relativistic effects
- Wave-particle duality
- Kinematics and dynamics
These concepts illustrate the diverse ways speed is manifested in the physical world, offering a deeper understanding of the forces that govern the universe.
Communication: How Fast is Fast?
The speed of communication has transformed the way we interact, share information, and conduct business. From the days of telegraphs and postal services to the era of instant messaging and video calls, communication technologies have evolved to offer near-instantaneous connections across the globe.
Modern communication tools rely on high-speed networks and data transmission methods, such as fiber optics and satellite communications, to deliver information with minimal delays. These technologies enable real-time communication, facilitating everything from remote work to international trade.
Factors Enhancing Communication Speed
- Broadband internet access
- Mobile network advancements
- Compression algorithms
- Cloud computing
As communication continues to evolve, the focus remains on increasing speed while maintaining reliability and security, ensuring that information flows seamlessly in an increasingly connected world.
The Speed of Computing: Past, Present, Future
Computing speed has seen exponential growth, with advancements in hardware and software driving unprecedented performance levels. From the early days of vacuum tube-based machines to today's supercomputers, computing speed has transformed industries and research fields.
The introduction of microprocessors and integrated circuits marked a significant leap in speed, enabling personal computers and mobile devices to become ubiquitous. Modern processors, with multiple cores and high clock speeds, support complex applications and multitasking.
Future Trends in Computing Speed
- Quantum computing
- Neuromorphic computing
- Artificial intelligence acceleration
- Edge computing
These trends promise to further enhance computing speed, offering new possibilities for innovation and problem-solving in various domains.
Entertainment: Where Does Speed Take the Lead?
Speed in entertainment is often associated with thrilling experiences and high-energy performances. From fast-paced action films and video games to live sports events, speed captivates audiences and adds excitement to the entertainment industry.
In gaming, advancements in graphics processing and internet speeds have enabled immersive experiences, with fast-paced gameplay and real-time multiplayer interactions. In film and television, high-speed cameras and editing techniques create dynamic visuals that capture viewers' attention.
Speed-Driven Entertainment Trends
- Virtual reality experiences
- Esports competitions
- Interactive storytelling
- Streaming services
These trends highlight the role of speed in shaping the future of entertainment, offering audiences new ways to engage with content and experience high-speed thrills.
Speed and Safety: Where Do They Intersect?
The relationship between speed and safety is complex, with higher speeds often associated with increased risks. In transportation, speed limits and safety regulations aim to balance efficiency with the protection of passengers and pedestrians.
In the workplace, speed can lead to efficiency but also poses risks if safety protocols are not followed. Industries such as manufacturing and construction implement safety measures to mitigate the hazards associated with fast-paced environments.
Strategies for Balancing Speed and Safety
- Implementing speed limits and traffic laws
- Promoting workplace safety training
- Using technology for monitoring and enforcement
- Encouraging a culture of safety awareness
These strategies emphasize the importance of maintaining safety while leveraging the benefits of speed, ensuring that progress does not come at the expense of well-being.
Historical Speed Milestones
Throughout history, speed has been a driving force behind many significant milestones and achievements. The invention of the wheel, the development of steam engines, and the advent of powered flight are just a few examples of how speed has shaped human progress.
The Space Race epitomized the quest for speed, with both the United States and the Soviet Union striving to achieve rapid advancements in space exploration. The successful landing of humans on the moon in 1969 marked a pinnacle of speed and technological achievement.
Key Historical Speed Milestones
- Introduction of the steam locomotive
- First powered flight by the Wright brothers
- Breaking the sound barrier
- Lunar landing of Apollo 11
These milestones reflect humanity's relentless pursuit of speed and the transformative impact it has had on society and the world.
What Does the Future Hold for Speed?
The future of speed is filled with potential, driven by ongoing advancements in technology, science, and innovation. As we continue to push the boundaries of what's possible, speed will remain a key factor in shaping our world.
Emerging technologies such as quantum computing, hypersonic travel, and advanced propulsion systems hold the promise of even greater speeds, revolutionizing industries and exploring new frontiers. However, the pursuit of speed must be balanced with considerations of sustainability and ethical implications.
Future Opportunities and Challenges
- Development of sustainable technologies
- Addressing ethical concerns in AI and automation
- Ensuring equitable access to high-speed technologies
- Balancing innovation with environmental stewardship
These opportunities and challenges highlight the dynamic nature of speed and its potential to inspire progress and change in the future.
FAQs about Speed Examples
1. What is the fastest recorded speed by a human?
The fastest recorded human running speed is 27.8 mph, achieved by Usain Bolt during a 100-meter sprint.
2. How do animals achieve such high speeds?
Animals achieve high speeds through a combination of physical adaptations, such as lightweight bodies, powerful muscles, and specialized structures for efficient movement.
3. What is the significance of the speed of light?
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics, representing the maximum speed at which information and energy can travel in the universe.
4. How has technology improved communication speed?
Technology has improved communication speed through advancements in network infrastructure, data transmission methods, and mobile connectivity, enabling near-instantaneous communication.
5. What are some examples of speed in sports?
Examples of speed in sports include sprinting events in track and field, fast-paced team sports like soccer and basketball, and speed-based competitions in motorsports.
6. How is speed measured in physics?
In physics, speed is measured as the rate of change of position with respect to time, typically expressed in units such as meters per second (m/s) or miles per hour (mph).
Conclusion
Speed examples across various domains illustrate the diverse ways in which speed influences our world. From the natural agility of animals to the technological advancements driving innovation, speed is a dynamic and multifaceted phenomenon. As we continue to explore the possibilities of speed, we must balance the pursuit of velocity with considerations of safety, sustainability, and ethical implications. The future of speed promises exciting developments and challenges, shaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.